Context Of Sustainability
For Magarpatta City Group
We have not just introduced environmental protection practices at our projects, we have also included them as one of the important objectives of our policy framework. It has helped create unique identities for all our projects. Following are the details on the sustainability initiatives at Magarpatta City.
The same model has been used at Nanded City, Pune and will also be implemented at Riverview City.
Sustainability Organogram
of Magarpatta City
Magarpatta City's commitment to foster leadership in sustainability and engage stakeholders along its supply chain is integral to the company's vision. With innovation at its core, Magarpatta City strives to practice the triple bottom line approach to sustainability- contributing to sustainable development as well as economic success.
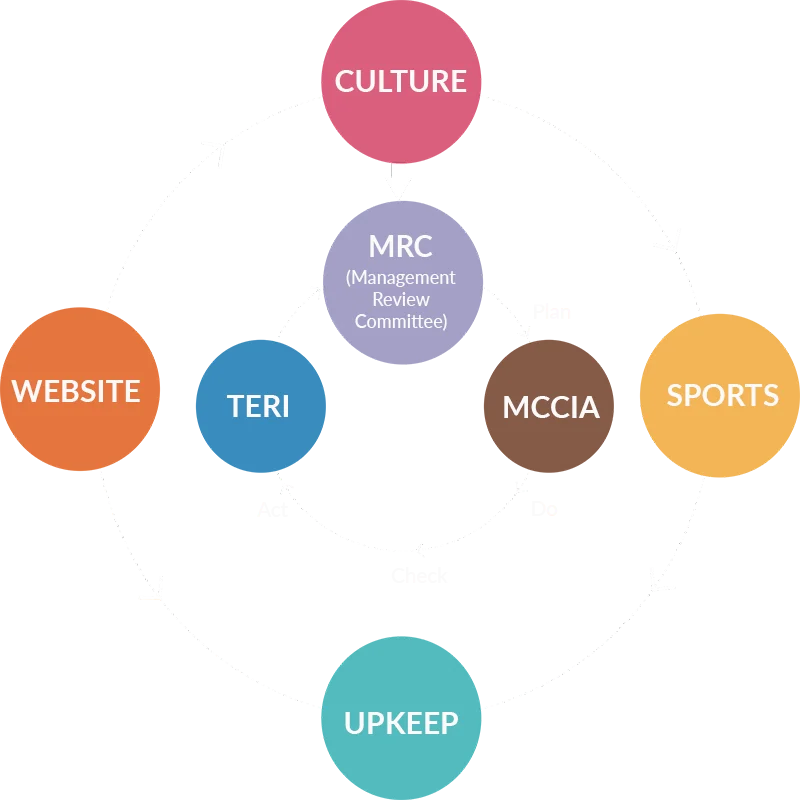
The City Council, with one representative for every 75 citizens, oversees the regular operations of the city. Alongside the council, a set of four committees—Culture, Sports, Upkeep and Website—provide feedback and inputs to improve the quality of services. The sustainability issues pertaining to Magarpatta City are regularly deliberated amongst the citizen representatives through these committees.
The Corporate Sustainability team of Magarpatta City is led by a Steering Committee constituting Mr. Satish Magar, MD (Chairman), along with an advisory role of TERI and MCCIA.
Alongside the monthly Management Review meetings, the Steering Committee deliberates, articulates and reviews performance of the sustainability framework for Magarpatta City.
JAL
(WATER)
PRUTHVI
(EARTH)
VAYU
(WIND)
AGNI
(FIRE)
AAKASH
(SKY)
ECO-ETHICS BY
MAGARPATTA CITY
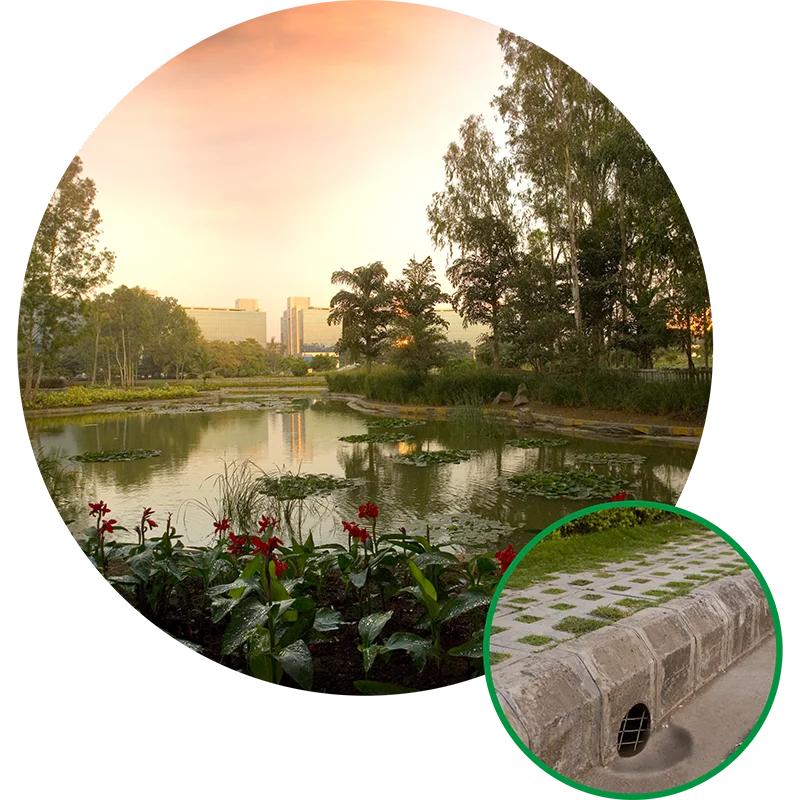

Rainwater Harvesting
and Recharging
Groundwater
Rainwater harvesting, an eco-friendly method, is extensively practiced at Magarpatta City. Rainwater is collected, which recharges groundwater and increases the water table. The water that would otherwise have gone down the drainage system into the ground or have been lost through evaporation is used for this purpose. Footpath and landscaping pavers are designed with cut-outs, which aid in absorbing water into the ground. Mounds are created out of the earth and excavated to increase the surface area, leading to more water retention. Even the compound has interlocking blocks instead of concrete, enabling rainwater to be absorbed instead of being drained away.
Before the township was established, Magarpatta City had 8 wells to irrigate the land. The rainwater harvesting systems are designed to recharge these wells. Some part of the collected rainwater is stored in an artificial lake at Aditi Garden, with the majority of collected rainwater injected into the 375 recharging borewells.
Passive Design Considerations to
Reduce Energy Loads of Buildings
Managing Carbon
Emissions in
Magarpatta City
The parking below Cybercity is semi-raised to assist natural ventilation and enable exhaust from vehicles to be removed naturally without the help of any mechanical aid. Also, a space between the glass facade and internal windows is provided in all IT buildings to enable the heat to dissipate naturally by creating air insulation. The residential neighborhoods are built on the traditional 'Puneri Wada' concept to enable natural light and breeze to flow through.
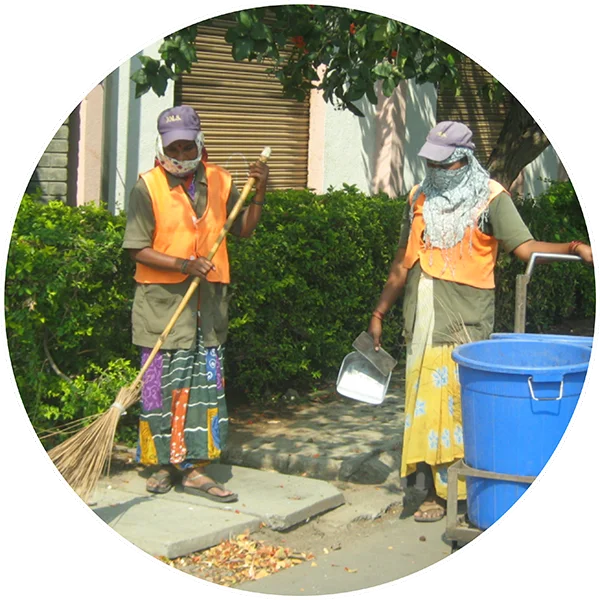

Garbage Collection
and Disposal
Every day, garbage is collected and treated within Magarpatta City and very little waste is sent out to landfills. Waste is segregated at source and bio-degradable waste is used to generate biogas, which in turn is used for power generation and composting. Non-biodegradable waste is disposed safely and reusable scrap is sold.